Eric Connelly
Trend and Noise
Introduction
Using Numpy and Matplotlib, we can generate graphs consisting of a deterministic trend and a random noise component. We will only be focusing on polynomial trends for this project. The noise will be sampled from a normal distribution.
Code
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def my_plot(
#The x-axis bounds of our graph will be -T , T.
T = 5,
# Controls the granulairty of the x-axis.
delta = 0.1,
#The standard deviation of the noise component;
#controls the "spread" of the noise.
sigma = 4,
#The coefficients of our polynomial trend.
bs = [2,-1,1,-0.5]
):
#The degree - 1
d = len(bs)
#The domain of our polynomial
ts = np.arange(-T , T + 1,step = delta)
#Generating the values for each term in our polynomial.
s = 0
for i in range(d):
s += (ts**i * bs[i])
#Adding on the noise component.
x = s + np.random.normal(0,sigma,len(ts))
#Plotting
plt.scatter(ts,x)
plt.plot(ts,s,color = 'r')
plt.grid(True)
plt.show()
Examples
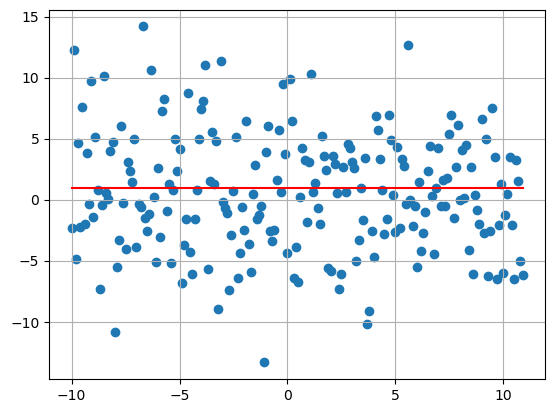
#Cubic Trend
my_plot(
T = 5,
delta = 0.1,
sigma = 4,
bs = [0.2,-1,1,-1]
)
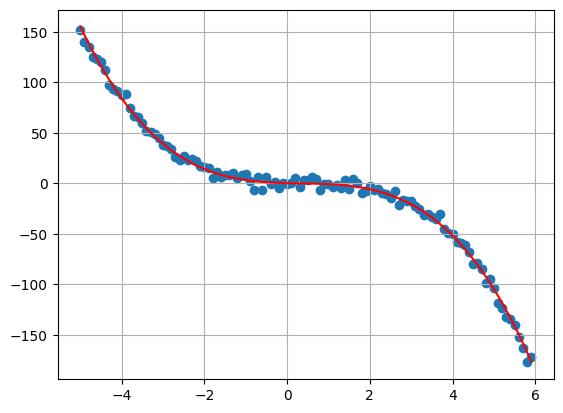
#Qudratic Trend
my_plot(
T = 5,
delta = 0.1,
sigma = 4,
bs = [0,-1,1]
)
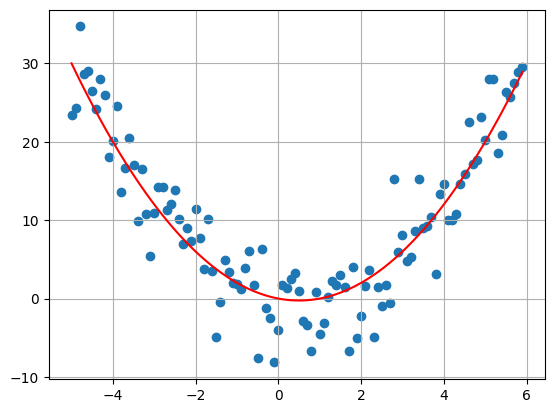
#Linear Trend
my_plot(
T = 5,
delta = 0.1,
sigma = 4,
bs = [0,1]
)
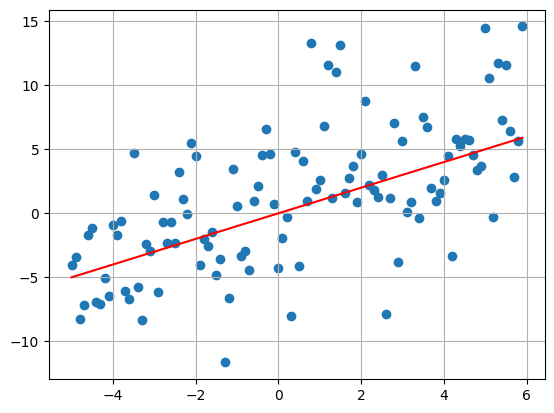
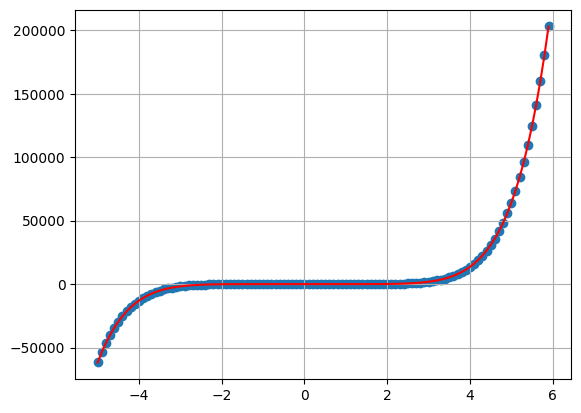
#8 Coefficients
u = np.random.uniform(-1,1,size = 8)
my_plot(
T = 5,
delta = 0.1,
sigma = 2,
bs = u
)
print(u)
[-0.60451821 0.52492362 -0.93467623 0.47131298 0.11940715 0.20363388
0.07282746 0.79642811]